Hernia Care And treatment
Jul 08, 2023
Have you ever had an odd bulge or pain in your abdomen or groin?
If so, you may have had a hernia. Hernia can occur at any age or gender and can be caused by a variety of reasons. But don't panic, hernias can be properly treated and even cured with correct diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will go over the basics of hernias, from what they are to how they are treated, as well as some prevention suggestions.
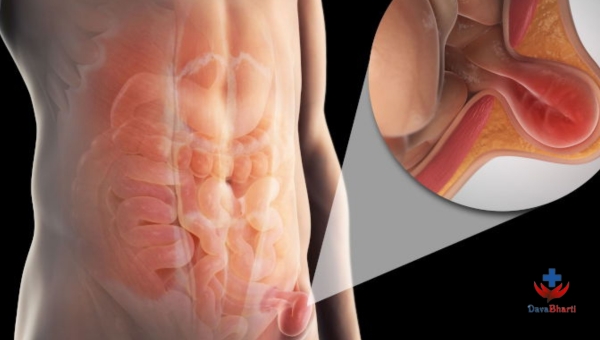
Hernia
A hernia is a medical problem that arises when organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective that typically holds the organ or tissue in place.The most frequent type of hernia is the inguinal hernia, which develops in the groin area although it can also occur in other parts of the body such as the belly abdomen, diaphragm or navel.

Causes of Hernias
Although the exact origin of a hernia is not always known, several common variables that can contribute to hernia development include:
Weakness in the abdominal wall: Hernias commonly occur where the abdominal wall muscles are weak.
Age: As we get older, the muscles and tissues that support the abdominal wall weaken, making a hernia more likely.
Genetics:Many people may be sensitive to acquiring due to a family history of the condition.
Straining:Straining during bowel motions, urinating, or moving heavy objects can increase abdominal cavity pressure and increase the likelihood of a hernia developing.
Pregnancy:The strain placed on the abdominal wall by a growing fetus can weaken the muscles and tissues, increasing the likelihood of a hernia developing.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts additional strain on the abdominal wall, increasing our risk of developing a hernia.
Chronic coughing or sneezing: These actions can put stress on the abdominal muscles, leading to a hernia.
Symptoms of Hernia:
Pain or Discomfort: Hernias can cause burning sensation or dull ache in the affected area, especially during lifting or bending.
A feeling of heaviness or pressure: Many people may experience a sense of pressure or fullness in the abdomen or groin area or abdomen.
Nausea and vomiting: In many cases, a cause of a hernia can be nausea and vomiting, especially if the hernia is blocking the digestive tract.
Difficulty passing stool or urine: A hernia that has grown large enough to press against the intestines or bladder can make passing stool or urine difficult.
Inability to push the hernia back in: In some circumstances, the hernia may be reducible, which means it can be pushed back into place. If the hernia becomes entrapped, it cannot be pulled back in and may necessitate emergency medical treatment.

Treatment of Hernia
- Non-surgical treatment: For small, asymptomatic hernias that are not causing any difficulties. Your doctor may prescribe cautions waiting for minor .This involves examining the hernia for any changes and addressing any accompanying symptoms.Wearing a supporting device, such as a truss or binder, may also be recommended to help support the affected area.
- Surgical treatment:Surgery may be recommended if the hernia is big and causing substantial discomfort or consequences, or if watchful waiting is not an option. A hernia can be repaired using a variety of surgical techniques, including open surgery and minimally invasive treatments like laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery.
Hernia Diagnosed
A hernia is normally diagnosed during a physical examination by a doctor, who will look for evidence of a bulge in the affected area. The doctor may also inquire about your symptoms, such as pain or discomfort in the affected area.
In some cases, imagine tests may be order to confirm the diagnosis or to assess the severity of the hernia. These tests may include:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive exam generates images of the afflicted area using high-frequency sound waves.
- CT scan: A computerized tomography (CT) scan uses a combination of computer technology and X-raysto createthe detailed images of the affected area.
- MRI: A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan uses a improvise magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the affected area.
Hernia Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being heavyweight or obese can increase your risk of developing a hernia. Maintaining a healthy weight through a normal diet and daily exercise can help to reducing this risk.
- Practice good posture: Poor postures can put additional strain on your muscles and increase your chances of having a hernia. Maintainproper posture while standing or sitting, and avoid heavy lifting or straining.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects: Lifting heavy objects can place a lot of strain on your muscles, especially those in your abdominal area. When carrying something large, employ proper lifting techniques and avoid twisting or bending at the waist.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can weak your muscles and increase your chance of developing a hernia. If you smoke, quitting can help to reduce your risk.
- Treat constipation: Straining during bowel motions increases the likelihood of getting a hernia. To lessen this risk, eat a high-fiber diet and remain hydrated to help prevent constipation.
- Treat Chronic cough: Cough that has been present for a long time due to various causes such as tuberculosis, and bronchitis may cause increase in abdominal pressure leadsto hernia.
- Consult your Physician: If you have a family history of hernias or have had a hernia in the past, talking to your doctor about ways to lower your risk and any necessary precautions you should take.
Getting the medical treatment and care is crucial to avoid any associated medical complications.
Recent Post
Ayurvedic Remedies To Manage High Blood Pressure

Best Ayurvedic Tips for Weight Loss

How to Store Medicines at Home Safely and Effectively

Your Ultimate Guide To A Balanced Diet For Diabetes

Ayurvedic Skincare Tips: Say Goodbye to Dry & Itchy Skin This Winter

Winter Wellness: Staying Healthy During the Cold Months

Natural Remedies for Mental Wellness Top Ayurvedic Solutions

Men’s Health Awareness: Natural Approaches to Boost Energy, Vitality, Prostate Health, and Mental Wellness

Overweight and Obesity: Causes, Impact, and Solutions

Detoxing Your Body: A Natural Path to Health and Wellness